helloworld.py - How to run Python Sample Code using the Hello World API and Mutual SSL
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
helloworld.py - How to run Python Sample Code using the Hello World API and Mutual SSL
In this "How-to" guide we will show you how to run the “Hello World” project using Visa Hello World API and Two-Way SSL (Mutual Authentication). The Hello World API is a simple API for testing the connectivity with the Visa Network.
Important Links:
- The endpoint for the Hello World API is https://sandbox.api.visa.com/vdp/helloworld
- How to work with Two Way SSL Docs: https://developer.visa.com/pages/working-with-visa-apis/two-way-ssl
- Login to Visa’s developer portal or sign up to https://developer.visa.com/
How to Create a Visa Developer Project
Before you are able to run the “Hello World” Project, you must create a Visa Developer Portal (VDP) project and get credentials. If you haven't registered yet just click on register here, fill out the account information, agree to the terms and conditions and click on receive emails. Once you have successfully activated your account, you will see your dashboard and you are ready to go.
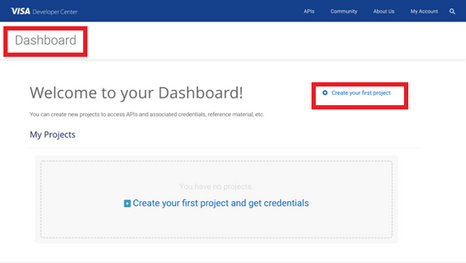
Once you are there, click on create your first project if this is your first project. On the next page, you will be asked for details, such as project name, description and a list of APIs to choose from.
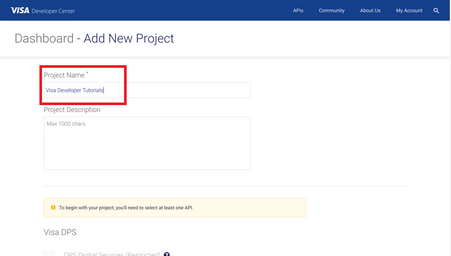
For this tutorial, we're going to select “Visa Direct” and click create project.
How to get Credentials
After creating your project, you will be redirected to the project summary page. You can obtain your project credentials by browsing the left side navigation menu of your project and click on “Credentials”.

What is required for the Two-Way SSL (Mutual Authentication)?
To be able to make an API call with 2-way SSL authentication, you need to have the following:
- User ID
- Password
- Your client cert
- Your private key previously downloaded
- Visa Development Platform Certificate

You will need to download the project certificate as well as the common certificates - Visa Developer Platform certificate and DigiCert Certificate and save them in the correct directory.
How to run the Python Sample code of the “Hello World API” using PyCharm
Next, we'll show you how to run the Python sample code of the “Hello World API” using PyCharm. PyCharm is a dedicated Python Integrated Development Environment (IDE) providing a wide range of essential tools for Python developers and can be downloaded using below link:
https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/download
In PyCharm, a project helps you organize your source code, tests, libraries that you use, build instructions, and your personal settings in a single unit.
Step 1 - Launch PyCharm
- On the PyCharm Welcome Screen, click Create New Project.
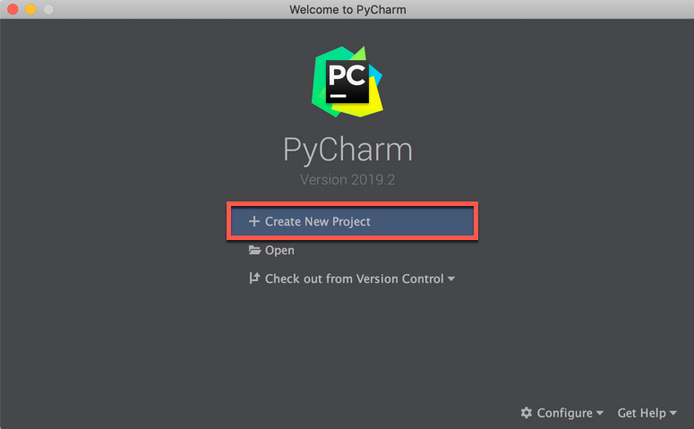
Otherwise, from the main menu, select File | New | Project
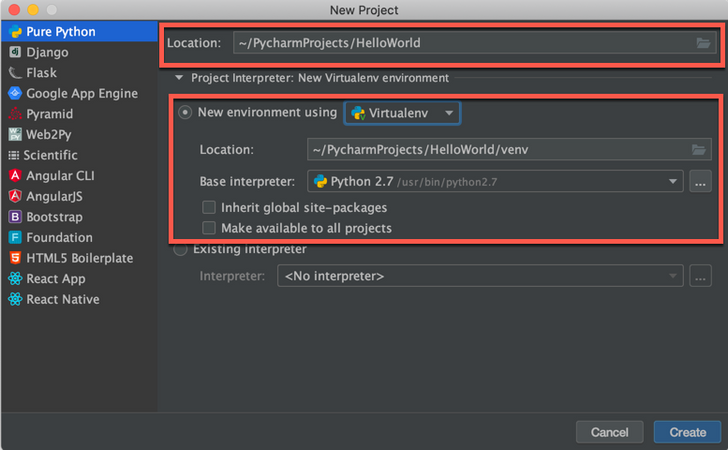
Step 2 - In the New Project wizard, select Pure Python from the list on the left, provide the project Location and click Create.
Please make sure to specify your “Project Interpreter”
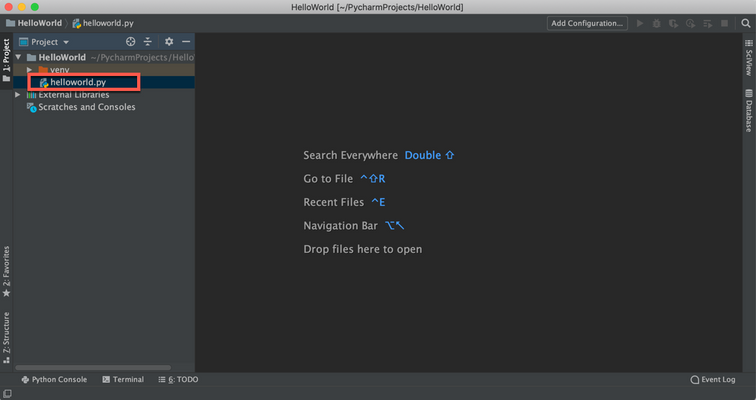
Step 3 - Create a new file and named it “helloworld.py”
Step 4 - Copy the below sample code to the “helloworld.py” file
- Install all the required dependencies when prompt.
- Set the below parameters:
user_id = '<YOUR USER ID>'
password = '<YOUR PASSWORD>'
cert = '<YOUR CLIENT CERTIFICATE PATH>'
key = '<YOUR PRIVATE KEY PATH>'
# *(c) Copyright 2018 - 2020 Visa. All Rights Reserved.**
#
# *NOTICE: The software and accompanying information and documentation (together, the “Software”) remain the property of and are proprietary to Visa and its suppliers and affiliates. The Software remains protected by intellectual property rights and may be covered by U.S. and foreign patents or patent applications. The Software is licensed and not sold.*
#
# * By accessing the Software you are agreeing to Visa's terms of use (developer.visa.com/terms) and privacy policy (developer.visa.com/privacy).In addition, all permissible uses of the Software must be in support of Visa products, programs and services provided through the Visa Developer Program (VDP) platform only (developer.visa.com). **THE SOFTWARE AND ANY ASSOCIATED INFORMATION OR DOCUMENTATION IS PROVIDED ON AN “AS IS,” “AS AVAILABLE,” “WITH ALL FAULTS” BASIS WITHOUT WARRANTY OR CONDITION OF ANY KIND. YOUR USE IS AT YOUR OWN RISK.** All brand names are the property of their respective owners, used for identification purposes only, and do not imply product endorsement or affiliation with Visa. Any links to third party sites are for your information only and equally do not constitute a Visa endorsement. Visa has no insight into and control over third party content and code and disclaims all liability for any such components, including continued availability and functionality. Benefits depend on implementation details and business factors and coding steps shown are exemplary only and do not reflect all necessary elements for the described capabilities. Capabilities and features are subject to Visa’s terms and conditions and may require development,implementation and resources by you based on your business and operational details. Please refer to the specific API documentation for details on the requirements, eligibility and geographic availability.*
#
# *This Software includes programs, concepts and details under continuing development by Visa. Any Visa features,functionality, implementation, branding, and schedules may be amended, updated or canceled at Visa’s discretion.The timing of widespread availability of programs and functionality is also subject to a number of factors outside Visa’s control,including but not limited to deployment of necessary infrastructure by issuers, acquirers, merchants and mobile device manufacturers.*
#
import datetime
import json
import logging
import requests
# DEBUG = False
DEBUG = True
# helloworld
# Sample Code for Two-Way (Mutual) SSL
# These two lines enable debugging at httplib level (requests->urllib3->http.client)
# You will see the REQUEST, including HEADERS and DATA, and RESPONSE with HEADERS but without DATA.
# The only thing missing will be the response.body which is not logged.
try:
import http.client as http_client
except ImportError:
# Python 2
import httplib as http_client
http_client.HTTPSConnection.debuglevel = 0
# You must initialize logging, otherwise you'll not see debug output.
logging.basicConfig()
logging.getLogger().setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
requests_log = logging.getLogger("requests.packages.urllib3")
requests_log.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
requests_log.propagate = True
print("START Sample Code for Two-Way (Mutual) SSL")
print(datetime.datetime.now())
date = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S")
url = 'https://sandbox.api.visa.com/vdp/helloworld'
headers = {}
body = {}
payload = json.loads('''{}
''')
# THIS IS EXAMPLE ONLY how will user_id and password look like
# user_id = '1WM2TT4IHPXC8DQ5I3CH21n1rEBGK-Eyv_oLdzE2VZpDqRn_U'
# password = '19JRVdej9'
user_id = '<YOUR USER ID>'
password = '<YOUR PASSWORD>'
# THIS IS EXAMPLE ONLY how will cert and key look like
# cert = 'cert.pem'
# key = 'key_83d11ea6-a22d-4e52-b310-e0558816727d.pem'
cert = '<YOUR CLIENT CERTIFICATE PATH>'
key = '<YOUR PRIVATE KEY PATH>'
timeout = 10
try:
response = requests.get(url,
# verify = ('put the CA certificate pem file path here'),
cert=(cert, key),
# headers = headers,
auth=(user_id, password),
# data = body,
# json = payload,
timeout=timeout
# if DEBUG: print (response.text)
)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
if DEBUG: print(response.headers)
if DEBUG: print(response.content)
var1 = str(response.status_code)
var2 = '200'
msg = " Two-Way (Mutual) SSL test failed"
assert var1 == var2, msg
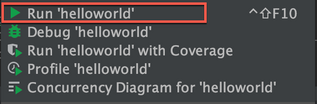
Step 5 - Compile Your Code
- Simply right click and run “helloworld”
Want more? Join the Visa Developer Community to get alerts on the latest tutorials, guides and new developer resources. Stay tuned for more in the series.

