How to test and troubleshoot APIs with the Visa Developer Center Playground
We feel that the Visa Developer Center has come full circle since launch in 2016. It hosts many APIs...
Mutual Authentication, also commonly referred to as Two-Way Authentication or Two-Way SSL, refers to the combination of both Server and Client Authentication. The authentication is mutual, or two-way, because the server is authenticating itself to the client, and the client is authenticating itself to the server in order to establish a secure encrypted channel between them.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is used to secure communications over a network so that only the sender and receiver have access to the sensitive data that is contained within. This is done with the use of Certificates and Keys. A Certificate contains basic information and a digital signature that properly identifies the client or server that it is associated with. Keys comprise of public, private, and session working together to establish an encrypted connection.
Example
If you have ever bought something from Amazon, you have used SSL. During checkout, you may have noticed the little padlock icon () in the status bar of your web browser, or that the URL field of your browser begins with https. This indicates that you are communicating with the website’s server through SSL to secure your personal information, your credit card number, etc. This type of SSL between a web browser and a website server includes what is commonly known as Server Authentication described below.
Server Authentication is a means of authenticating and identifying the server to the client using a Server Certificate. A Server Certificate is a required part of any SSL communication. The server certificate contains basic information and digital signature that properly identifies the server it is associated with.
Client Authentication, similar to server authentication is a means of authenticating and identifying the client to the server using a Client Certificate. A Client Certificate contains basic information about the client’s identity, and the digital signature on this certificate verifies that this information is authentic.
Steps for Mutual Authentication SSL
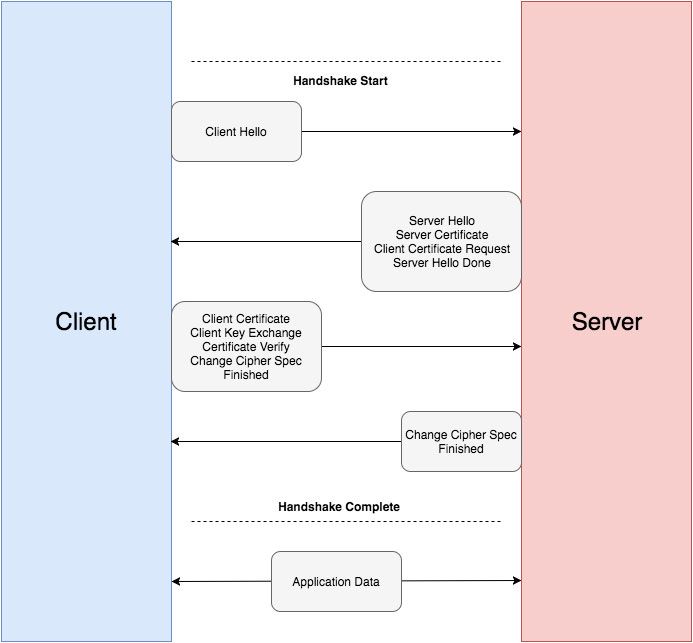
This sections lists the phase-wise steps for mutual authentication.
PHASE 1
In the first phase, Client connects to a web server (website) secured with SSL (https). The detailed steps are as follows:
Server sends the client certificate request only in the case of mutual authentication.
PHASE 2
In the second phase, Server validation is performed by the client. This is the Mutual or Two-Way Authentication.
PHASE 3
In this phase, Client validation is performed by the Server.
PHASE 4
In this phase, both Client and Server complete the handshake process so that they may begin sending application data.
Once a successful handshake is completed, the client and server will use the symmetric key for encrypting/decrypting data.
Here is a quick illustration of the phases described above:
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.
We feel that the Visa Developer Center has come full circle since launch in 2016. It hosts many APIs...
In this developer guide, we will show you how to test Message Level Encryption (MLE) enabled APIs us...
First time to the Visa Developer Center? Watch this tutorial to learn where to find the Visa APIs th...
Watch the recording of my How to Run a Visa Direct Transaction using Python webinar as you follow al...